Relative placement of objects I¶
Learning targets
- Relative and global placement of geometrical objects
- Alignment of object ports
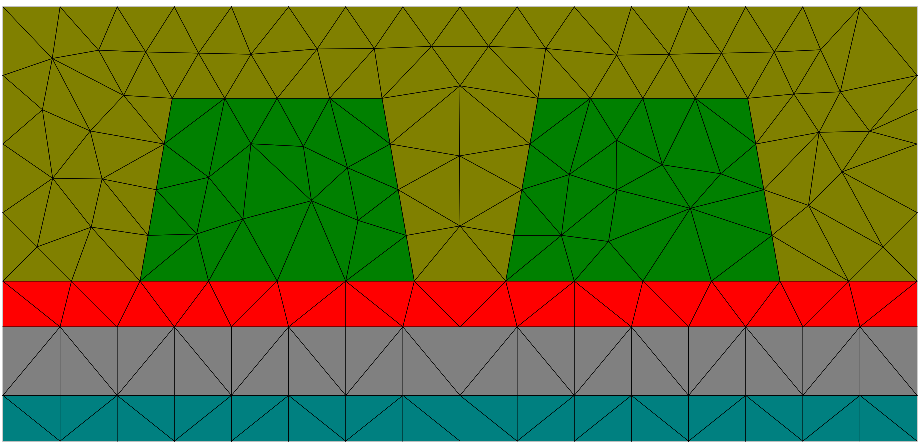
This example shows how to construct an optical coupler based on two rip waveguides.
The substrate consists of three layers which are aligned on top of each other. The rips are relatively aligned to the port North (upper center) of the top layer with a displacement to the left and right respectively.
.jcm Input File
layout.jcm [ASCII]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85
Layout2D { Name = "TutorialExample2D" UnitOfLength = 1e-06 MeshOptions { MaximumSideLength = 1 } Objects { Parallelogram { Priority = ComputationalDomain DomainId = 1 BoundingBox { Offset = [0 0 0 1] } } Parallelogram { Name = "Layer1" DomainId = 2 Height = 10 Width = 1 Port = South } Parallelogram { Name = "Layer2" DomainId = 3 Height = 10 Width = 1 Alignment { Parent { Domain = "Layer1" Port = North } Orientation = AntiParallel } } Parallelogram { Name = "Layer3" DomainId = 4 Height = 10 Width = 0.5 Alignment { Parent { Domain = "Layer2" Port = North } Orientation = AntiParallel } } Trapezoid { Name = "RipLeft" DomainId = 5 Height = 2 Width = 3 InnerAngles = [80 80] Port = South Alignment { Parent { Domain = "Layer3" Port = North } Orientation = AntiParallel Displacement = [-2 0] } } Trapezoid { Name = "RipRight" DomainId = 5 Height = 2 Width = 3 InnerAngles = [80 80] Port = South Alignment { Parent { Domain = "Layer3" Port = North } Orientation = AntiParallel Displacement = [2 0] } } } }