Transparent boundaries II¶
Learning targets
- Transparent boundary conditions
- Inhomogeneous exterior domain
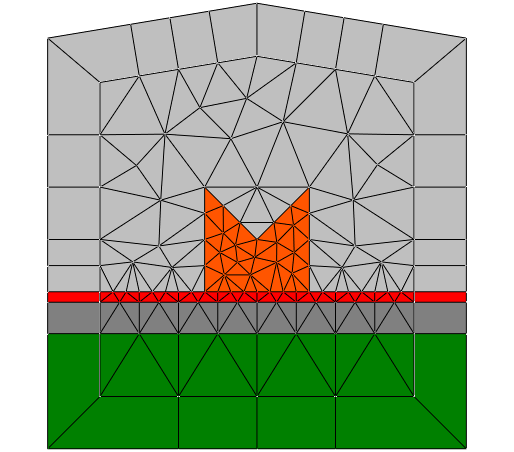
This example contains a 2D layout with transparent boundaries
on all faces of the computational domain. The lower part of the
computational domain contains a layered structure. Note that
JCMgeo automatically extends this layered structure to the
exterior domain.
I.e., this geometry models a single object placed
on a layered structure which extends to infinity.
The resulting geometry and mesh correspond to the following figure:
.jcm Input File
layout.jcm [ASCII]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46
Layout2D { Name = "TutorialExample2D" UnitOfLength = 1e-06 MeshOptions { MinimumMeshAngle = 20 MaximumSideLength = 1.5 } Objects { Polygon { Name = "ComputationalDomain/Background" DomainId = 1 Priority = -1 Points = [-3 -3, 3 -3, 3 3, 0 3.5, -3 3] Boundary { Class = Transparent } } Polygon { Name = "Object" DomainId = 2 Priority = 1 Points = [-1 -1, 1 -1, 1 1, 0 0, -1 1] MeshOptions { MaximumSideLength = 0.6 } } Polygon { Name = "Layer1" DomainId = 3 Priority = 1 Points = [-3 -1.2, 3 -1.2, 3 -1, -3 -1] } Polygon { Name = "Layer2" DomainId = 4 Priority = 1 Points = [-3 -1.8, 3 -1.8, 3 -1.2, -3 -1.2] } Polygon { Name = "Layer3" DomainId = 5 Priority = 1 Points = [-3 -3, 3 -3, 3 -1.8, -3 -1.8] } }