LatticeCopies¶
| Type: | section |
|---|---|
| Appearance: | optional |
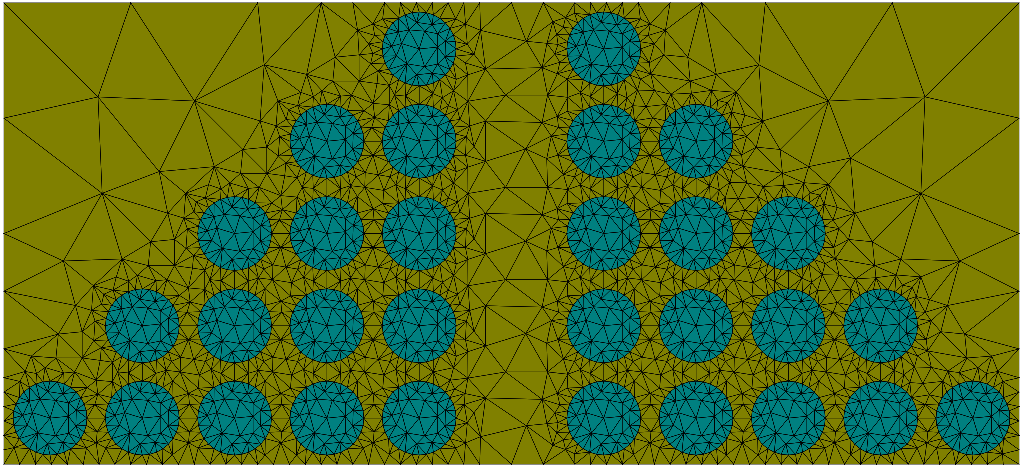
Many geometries like photonic crystals are constructed by a replication of a unit cell geometry at certain positions of a lattice. The following figure shows such a geometry with several circles copied to the lattice positions of a square lattice while omitting some lattice points (see the example in the GeoTutorial Lattice Copies):
A lattice is defined by two lattice vectors  and
and 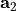 , the structures is replicated at positions displaced by
, the structures is replicated at positions displaced by
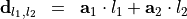
with integers  and
and  . The lattice vectors are defined by their lengths
. The lattice vectors are defined by their lengths ![[a_1, a_2]](_images/math/9aeeadf9d68dc7481831ac734d0df5c3a255e942.png) (LatticeVectorLengths) and the angle
(LatticeVectorLengths) and the angle 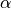 between them (LatticeAngle), that is
between them (LatticeAngle), that is
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\pvec{a}_1 & = & a_1\cdot[1; 0] \\
\pvec{a}_2 & = & a_2\cdot [\cos(\alpha); \sin(\alpha)].
\end{eqnarray*}](_images/math/89836b96330b5561f0cdbdc6382d694a972da3f4.png)
The lattice positions where the replicated geometry is actually placed can be defined in sub-sections Positions.