CMA_ES_Optimization¶
Purpose¶
The purpose of the driver is to identify a parameter vector 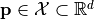 that minimizes the value of an objective function
that minimizes the value of an objective function 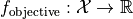 . The search domain
. The search domain 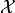 is bounded by box constraints
is bounded by box constraints 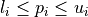 for
for 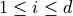 and may be subject to several constraints
and may be subject to several constraints 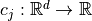 such that
such that 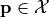 only if
only if 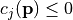 (see
(see create_study()).
The driver uses the heuristic CMA-ES method to search globally for a minimum of the objective function. We recommend to use Bayesian optimization to search globally for a minimum. Only if the evaluation times of the objective function are very short (smaller than 1-3 seconds) it can be beneficial to use CMA-ES.
The implementation of the driver is based on the open source implementation if CyberAgent, Inc. (see https://github.com/CyberAgentAILab/cmaes).
Usage Example¶
import sys,os
import numpy as np
import time
sys.path.append(os.path.join(os.getenv('JCMROOT'), 'ThirdPartySupport', 'Python'))
import jcmwave
client = jcmwave.optimizer.client()
# Definition of the search domain
domain = [
{'name': 'x1', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1.5,1.5)},
{'name': 'x2', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1.5,1.5)},
{'name': 'radius', 'type': 'fixed', 'domain': 2},
]
# Definition of a constraint on the search domain
constraints = [
{'name': 'circle', 'constraint': 'sqrt(x1^2 + x2^2) - radius'}
]
# Creation of the study object with study_id 'CMA_ES_Optimization_example'
study = client.create_study(domain=domain, constraints=constraints,
driver="CMA_ES_Optimization",
name="CMA_ES_Optimization example",
study_id='CMA_ES_Optimization_example')
# Definition of a simple analytic objective function.
# Typically, the objective value is derived from a FEM simulation
# using jcmwave.solve(...)
def objective(**kwargs):
time.sleep(2) # makes objective expensive
observation = study.new_observation()
x1,x2 = kwargs['x1'], kwargs['x2']
observation.add(10*2
+ (x1**2-10*np.cos(2*np.pi*x1))
+ (x2**2-10*np.cos(2*np.pi*x2))
)
return observation
# Set study parameters
study.set_parameters(max_iter=80, num_parallel=2)
# Run the minimization
study.set_objective(objective)
study.run()
info = study.info()
print('Minimum value {:.3f} found for:'.format(info['min_objective']))
for param,value in info['min_params'].items():
if param == 'x4': print(' {}={}'.format(param,value))
else: print(' {}={:.3f}'.format(param,value))
Parameters¶
The following parameters can be set by calling, e.g.
study.set_parameters(example_parameter1 = [1,2,3], example_parameter2 = True)
| mean0 (list): | Initial mean vector of multi-variate gaussian distributions. If not set, a random initial vector is chosen. (default: None) |
|---|
| sigma0 (float): | Initial standard deviation. The problem is internally rescaled such that all variables lie in the interval [0,1]. The standard deviation is defined on these rescaled variables. (default: 0.4) |
|---|
| population_size (int): | |
|---|---|
| The population size. (default: None) | |
| max_iter (int): | Maximum number of evaluations of the objective function (default: inf) |
|---|
| max_time (int): | Maximum run time in seconds (default: inf) |
|---|
| num_parallel (int): | |
|---|---|
| Number of parallel observations of the objective function (default: 1) | |
| eps (float): | Stopping criterium. Minimum distance in the parameter space to the currently known minimum (default: 0.0) |
|---|
| min_val (float): | |
|---|---|
| Stopping criterium. Minimum value of the objective function (default: -inf) | |