SourceSampling¶
| Type: | Matrix<float>, or section |
|---|---|
| Range: | [v_11, …, v_1j; …; v_i1, …; v_ij], j<=6 |
| Default: | -/- |
| Appearance: | simple |
Defines the source sampling of the illumination pupil in normalized 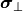 coordinates. For the notation see the parent section Illumination.
coordinates. For the notation see the parent section Illumination.
Each row in the matrix corresponds to a source point. The columns of the table must contain the following quantities: 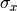 ,
, 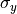 ,
, 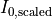 ,
, 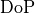 ,
,  , and
, and  . The quantities
. The quantities 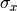 ,
, 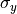 and
and 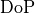 were introduced in the parent section Illumination. Instead of the intensity
were introduced in the parent section Illumination. Instead of the intensity 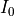 as introduced in the parent section Illumination a scaled intensity
as introduced in the parent section Illumination a scaled intensity 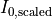 is passed. Details are given below.
is passed. Details are given below.
Together with the total intensity 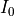 , the additional parameters
, the additional parameters  and
and  are used to fix the Jones vector components
are used to fix the Jones vector components 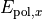 and
and 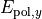 of the completely polarized state
of the completely polarized state 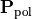 :
:
In general the completely polarized state exhibit a elliptical polarization with ellipticity given by  and orientation
and orientation  , so that
, so that
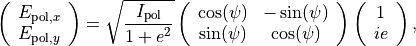
where 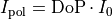 is the intensity of the completely polarized state.
is the intensity of the completely polarized state.
The completely unpolarized component
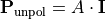
is determined from
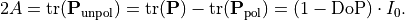
Warning
The given data, 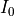 , etc, refer to the effective light source in the pupil plane.
, etc, refer to the effective light source in the pupil plane.
Note
The solver will enforce the following input bounds on the given source sampling matrix entries: 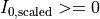 ,
, ![\mathrm{DoP}\in [0,1]](_images/math/161b68ca93ae683c03fa37029c8da373f98788f1.png) ,:math:psiin [0,1] and
,:math:psiin [0,1] and ![e \in [0,1]](_images/math/d7f4fa8a34b23214f6a131652c24ed99b0873d56.png)
Intensity scaling
It remains to fix the input quantity 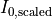 for a given source point
for a given source point  . In the parent section the total intensity
. In the parent section the total intensity 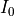 referred to the squared magnitude
referred to the squared magnitude 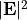 of the electric field vector of a plane wave. However, in many textbooks the intensity of a plane wave is defined as the magnitude of the Poynting vector, that is, as the energy flux through a unit surface perpendicular to the propagation direction.
of the electric field vector of a plane wave. However, in many textbooks the intensity of a plane wave is defined as the magnitude of the Poynting vector, that is, as the energy flux through a unit surface perpendicular to the propagation direction. JCMsuite uses the following convention:
The sum over all given scaled intensities  gives the total energy flux through the pupil plane:
gives the total energy flux through the pupil plane:
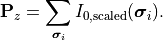
Hence, the scaled intensities already accounts for the integration of the extended illumination over the source points 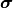 .
.