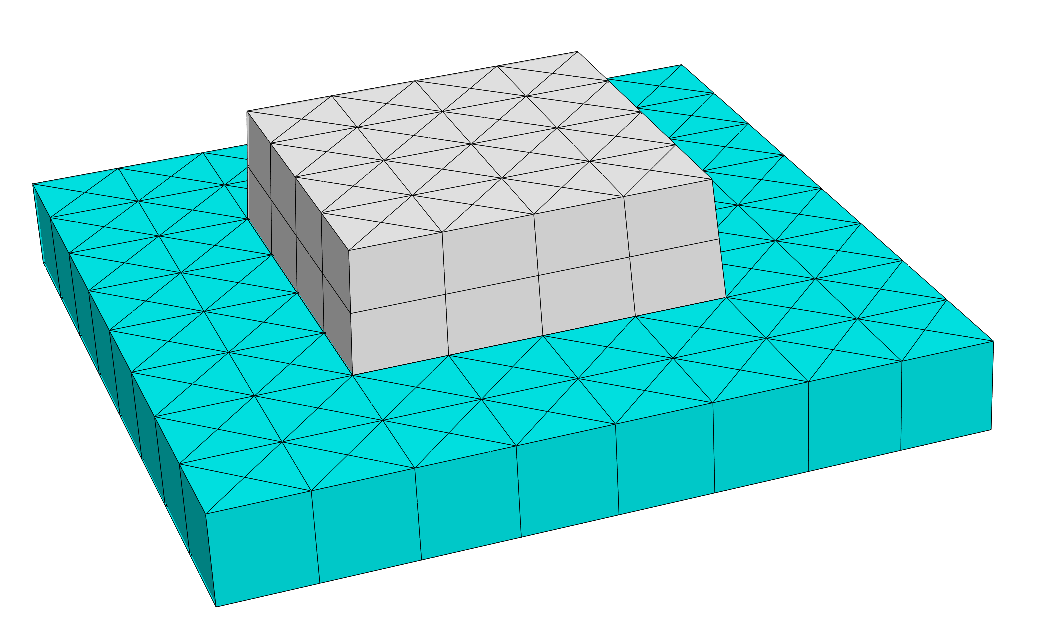
Square Unit Cell¶
This is a simple example of a 2D grating with a twofold periodic square lattice.
The 3D unit cell is periodic in 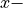 and
and 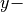 direction.
It contains a rhomboid (parallelepiped) situated on a substrate and surrounded by a background material.
The materials in the example are chosen as chrome (rhomboid), glass (substrate) and air (background).
direction.
It contains a rhomboid (parallelepiped) situated on a substrate and surrounded by a background material.
The materials in the example are chosen as chrome (rhomboid), glass (substrate) and air (background).
The grating is illuminated by plane waves with  and
and 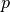 polarization.
polarization.
JCMsuite computes the near field distributions.
The following figures show the near-field intensities within the structure for
perpendicular plane wave incidence from the substrate side at a wavelength of 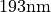 .
.
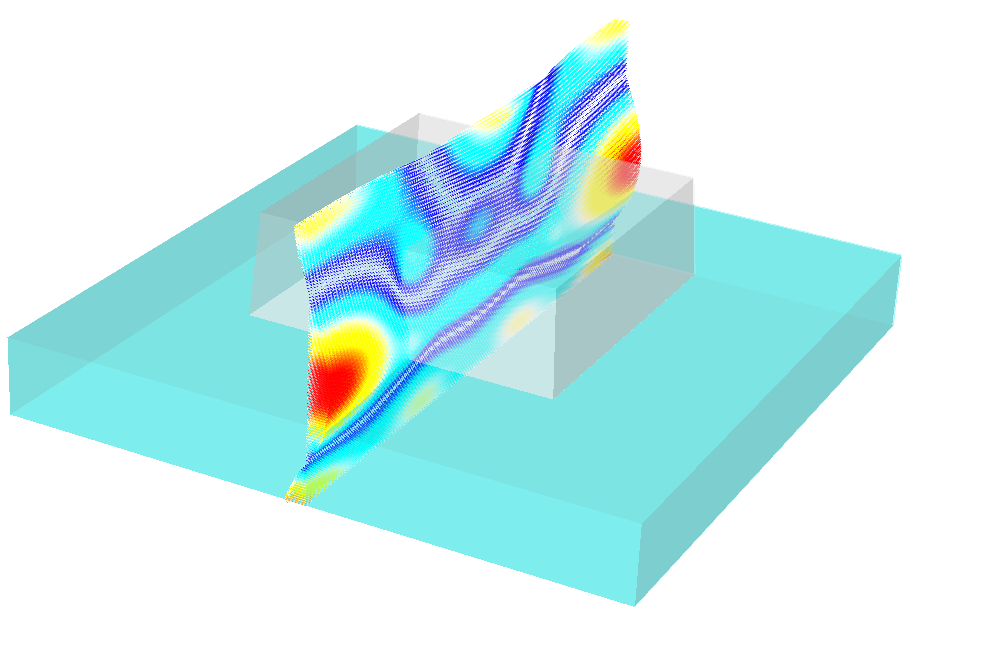
Field vectors for  -polarized illumination¶
-polarized illumination¶
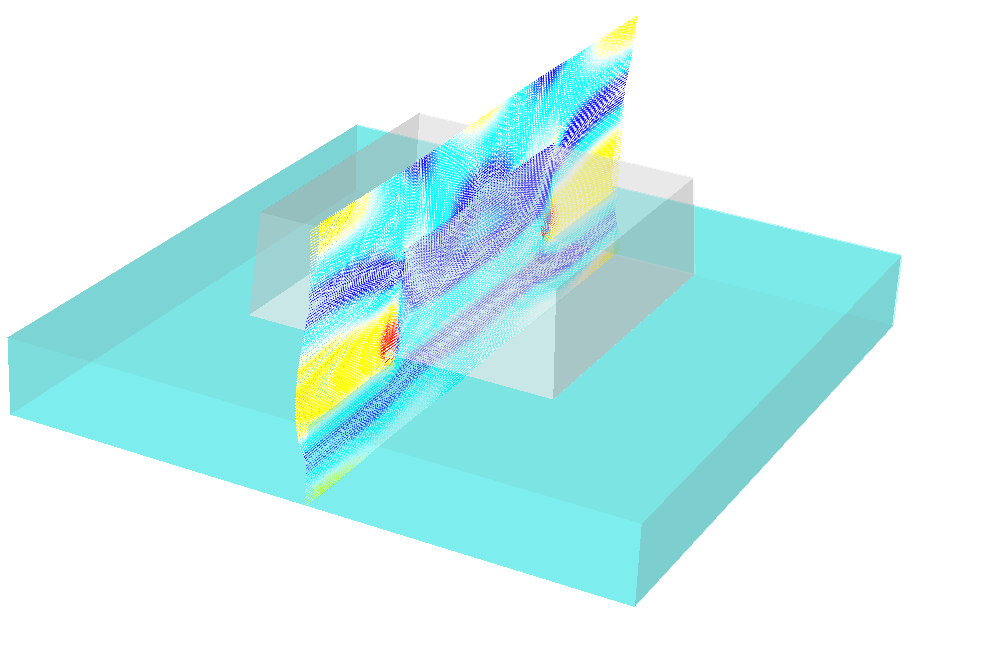
Field vectors for 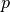 -polarized illumination¶
-polarized illumination¶
The post process FourierTransform computes the amplitudes of the transmitted diffraction orders.
Parameter scan
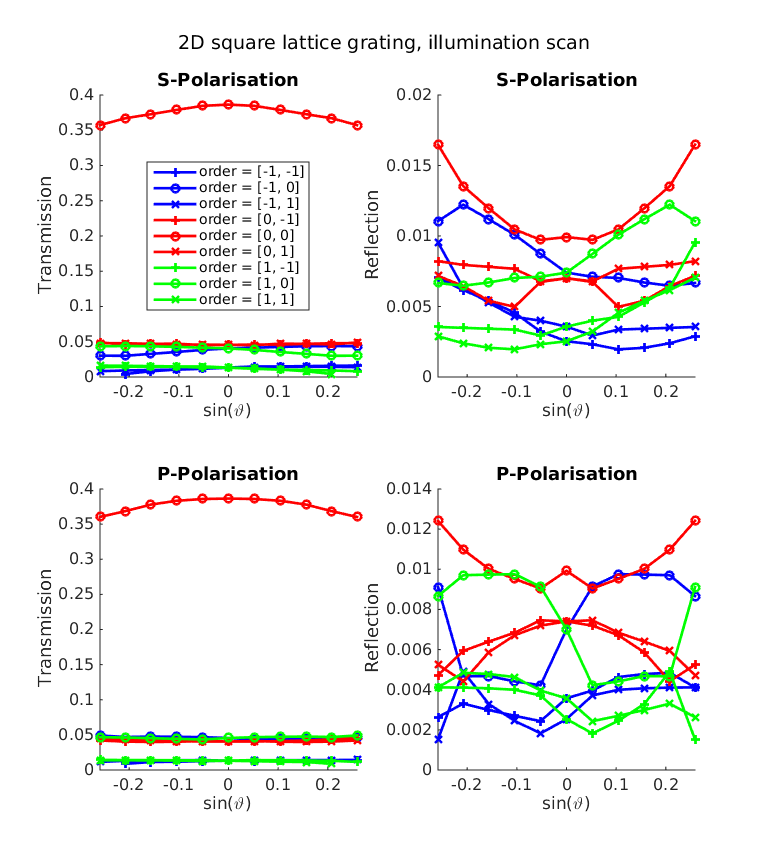
The Matlab® script data_analysis/run_scan_illumination.m provides a scan over the incidence angle.
It produces the following plots showing the intensities for reflected and transmitted diffraction orders:
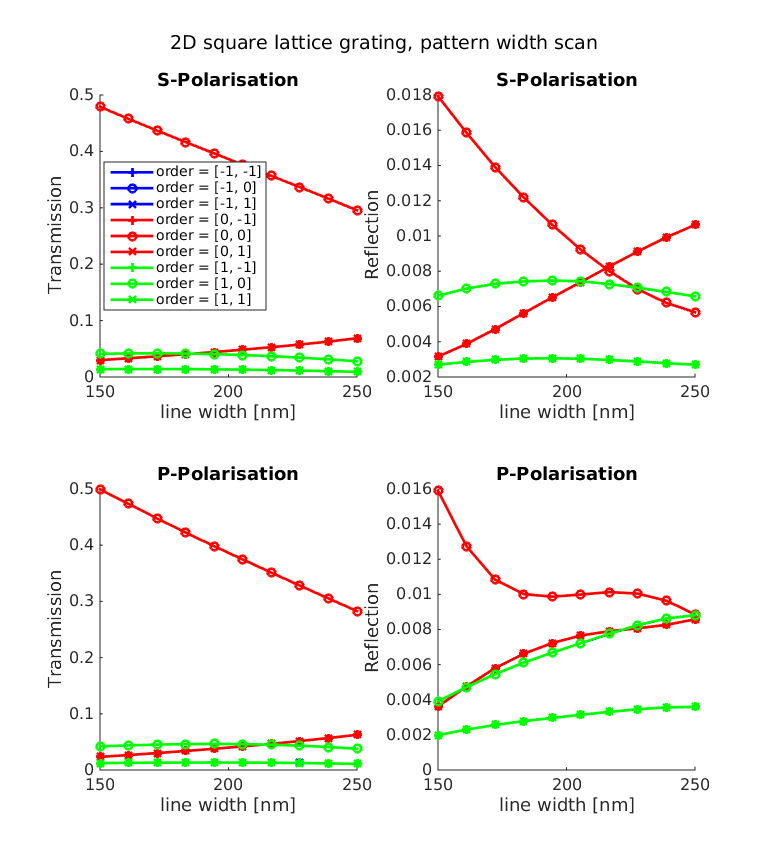
In the script data_analysis/run_scan_width.m the width of the pattern varies from 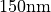 to
to 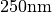 with fixed illumination angle.
This yields the following dependencies:
with fixed illumination angle.
This yields the following dependencies: