Displaying items by tag: light scattering computation
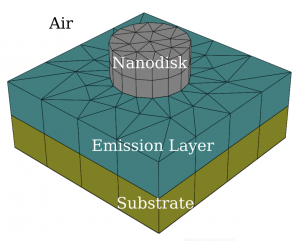
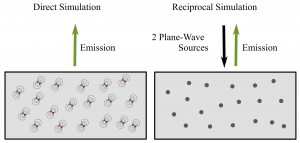
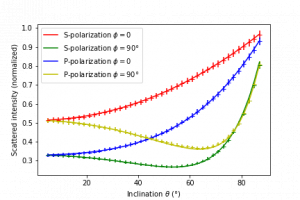
This post continues the series on modelling point dipole sources using reciprocity. It shows a concrete example of an ensemble of dipole emitters near a periodic nanostructure, which highlights the computational advantage of exploiting the receprocity theorem.
Published in Blog
This post continues the series on modelling point dipole sources. This post extends the application of the reciprocity theorem to dipoles separated by a large distance. Furthermore, the benefits of the use of the reciprocity principle are discussed.
Published in Blog
Tagged under
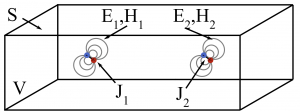
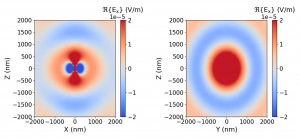
This post continues the series on modelling point dipole sources by discussing the application of the reciprocity principle to dipoles. In this post, the concept of reciprocity is introduced and applied to the near-fields of dipoles.
Published in Blog
Tagged under
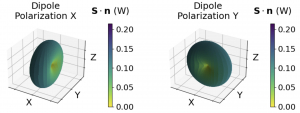
This is the second part of a series on dipoles. This post discusses how to evaluate the electromagnetic fields far away from the source. This is useful when modelling the spatial or angular distribution of light on a detector at a large distance form the source.
Published in Blog
Tagged under
Electric point dipole sources are, along with plane waves, one of the most commonly used sources types in electromagnetic computations. This first post on electric dipoles discusses their near-field properties both from both analytical expressions and numerical simulations in JCMsuite.
Published in Blog
Tagged under
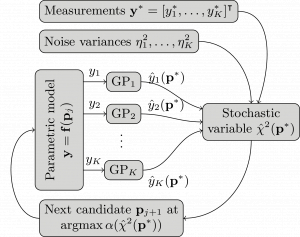
This is the third blog posts of a series dedicated to numerical methods for parameter reconstruction. In this postwe try to find the parameters with maximum likelidood based on a set of measurements. In order to do this with a small number of expensive simulations of the measurement process, we use the Bayesian least square method that is part of JCMsuite`s Analysis and Optimization Toolkit. Based on Gaussian process regression, the method learns the dependence of the measurements on the system paramters. This also allows to reconstruct the full posterior probability distribution of the system paramters given the measurement results.
Published in Blog
Tagged under
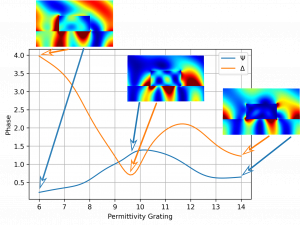
This is the second blog posts of a series dedicated to numerical methods for parameter reconstruction. An important question in the context of parameter reconstruction is how to setup an experimental measurement in order to retrieve enough meaningful information about the system parameters. This post describes the concept of variance-based sensitivity analysis which quantifies the sensitivity of the measurement process to the parameter values.
Published in Blog
Tagged under
This is the first blog posts of a series dedicated to numerical methods for parameter reconstruction. The overall goal is to determine the value of some system parameters, which are hard to measure directly, based on a set of more easily measurable observables and a numerical model of the measurement process. The first blog contains a brief introduction to the main concepts of parameter reconstruction while the following posts are dedicated to the application of some numerical methods and tools.
Published in Blog
Tagged under
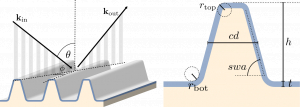
This blog post introduces the curvilinear element option for creating curved mesh elements. We assess under which conditions using a curvilinear degree is applicable and quantify the resulting inrease in accuracy.
Published in Blog
This blog post discusses defining the relative permittivity of materials in JCMsuite. Different methods for taking the frequency dependence of the permittivity into account are presented, including using a model and loading tabulated data from a file.
Published in Blog